Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Osawa, Hideaki; Koide, Kaoru; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Sato, Toshinori
Proceedings of 2015 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2015) (CD-ROM), p.371 - 378, 2015/04
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project, launched as a generic underground research laboratory for crystalline rock in 1996, has proceeded in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigation", "Phase II: Construction" and "Phase III: Operation". Currently, Phase II construction of research drifts in the MIU has been completed to the -500 m level. Phase III research activities have been conducted underground since 2010. The scientific and technical knowledge and know-how acquired in Phases I and II have been released via a web-based report "CoolRep H26". JAEA will continue to promote R&D activities in Phase III at the MIU to build technical confidence.
Liu, X.*; Ahn, J.*; Hirano, Fumio
Proceedings of 2015 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2015) (CD-ROM), p.879 - 886, 2015/04
The present work focuses on neutronics analysis for the disposal of damaged fuels from Fukushima Nuclear Power Plants. MCNP calculations were performed for a canister containing fuel debris surrounded by buffer in deep geologic repository in a water-saturated reducing environment at different times after canister emplacement. The damaged fuel debris is modeled as spherical particles in a hexagonal lattice. Four different cases were compared based on various assumptions about moderation and fuel relocation. Based on the numerical results, the key findings include, (a) the calculated neutron multiplication factor (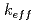 ) is sensitively dependent on assumptions related with moderation, (b) the carbon steel canister plays an important role in reducing the likelihood of criticality, (c) the maximum
) is sensitively dependent on assumptions related with moderation, (b) the carbon steel canister plays an important role in reducing the likelihood of criticality, (c) the maximum 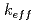 of the canister-buffer system could be achieved after a certain fraction of fissile nuclides has been released from the canister, and (d) under several assumptions, the maximum
of the canister-buffer system could be achieved after a certain fraction of fissile nuclides has been released from the canister, and (d) under several assumptions, the maximum 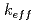 of the canister-buffer system could be only determined by the dimension and composition of the canister rather than the initial fuel loading.
of the canister-buffer system could be only determined by the dimension and composition of the canister rather than the initial fuel loading.